Road to Justice
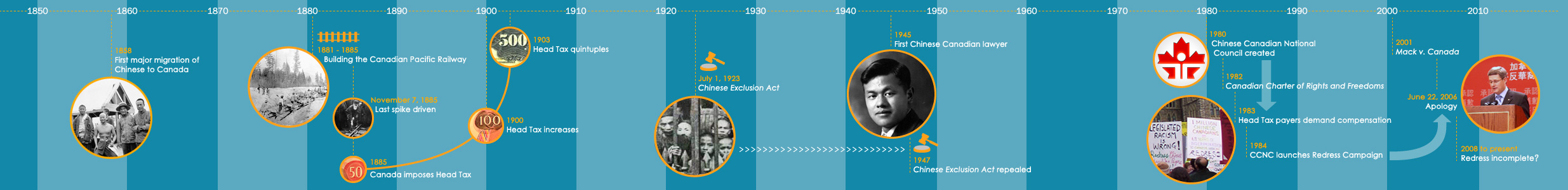
Road to Justice is an account of the historical use of law by governments in Canada as a tool to exclude, restrict or otherwise control the lives of people of Chinese descent. Road to Justice is undertaken by the Metro Toronto Chinese and Southeast Asian Legal Clinic with the support of the Government of Canada through the Community Historical Recognition Program.
This legal history project is in part an investigation of the social values and politics that led to such shameful laws as the Chinese Exclusion Act (Immigration Act, 1923) and the various head taxes on Chinese – which along with other federal, provincial, and municipal statutes – created a body of law that was aimed at restricting the lives and activities of a single race of people.
Selected decisions in key court cases are also summarized. The second part of Road to Justice covers interviews and biographical sketches of some of the first Chinese Canadian lawyers, as well as key activists in the Redress Campaign, who lobbied the Government of Canada for an apology for more than 60 years of legislated discrimination against them and their community.
These early laws were clearly discriminatory and they provide a stark contrast to the multiracial, multicultural Canada we share today with others from all parts of the world who have chosen this country as their home.